|
Online Merchandise
|
Google made the move to make all organic searches secure starting September 23, 2013. This means we have lost the ability to get keyword data for users arriving to our websites from Google Search. Losing Google keyword data is unfortunate for a number of reasons. This impacts publishers in many ways, including losing a valuable tool for understanding what the intent of customers that come to their site, for conversion optimization, and much more. For tactical SEO efforts, it just means that keywords data is harder to get. There are ways to work around this, for now, but it just won't be quite as simple as it used to be.
Historically, Google has updated the PageRank numbers shown in the Google Toolbar every 3 months ago or so, but those numbers haven't been updated since December 2013. In addition, Google's Distinguished Engineer Matt Cutts has said Toolbar PageRank won't be updated again this year, leading many to speculate that PageRank is going away. A lot of people still use it as a crude measurement of a site's prominence. For sites with a home page that has PageRank 7 or higher, it may in fact be reasonable to assume that the site has some chops. Correspondingly, sites with a home page that has a PageRank of 3 or lower, it is either new, or probably a low quality experience. Stuff in the middle, you just don't know. If Google shuts off this data flow entirely, which wouldn't be surprising, then they will have to rely on other real world measurements instead.
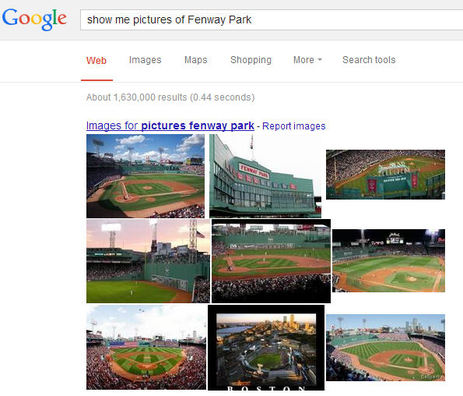
There are a few elements to Google's Hummingbird algorithm, announced in time for Google's official birthday, but like Caffeine before it, this is really a major platform change. Google has built a capability to understand conversational search queries much better than before. For example, submit a query to Google such as "show me pictures of Fenway Park", and it does, just like in the picture above.
Historically, Google has updated the PageRank numbers shown in the Google Toolbar every 3 months ago or so, but those numbers haven't been updated since December 2013. In addition, Google's Distinguished Engineer Matt Cutts has said Toolbar PageRank won't be updated again this year, leading many to speculate that PageRank is going away. A lot of people still use it as a crude measurement of a site's prominence. For sites with a home page that has PageRank 7 or higher, it may in fact be reasonable to assume that the site has some chops. Correspondingly, sites with a home page that has a PageRank of 3 or lower, it is either new, or probably a low quality experience. Stuff in the middle, you just don't know. If Google shuts off this data flow entirely, which wouldn't be surprising, then they will have to rely on other real world measurements instead.
There are a few elements to Google's Hummingbird algorithm, announced in time for Google's official birthday, but like Caffeine before it, this is really a major platform change. Google has built a capability to understand conversational search queries much better than before. For example, submit a query to Google such as "show me pictures of Fenway Park", and it does, just like in the picture above.
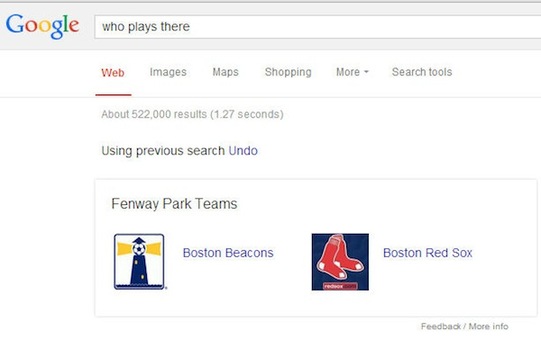
Then you can follow that query with this one: "who plays there", and you get this result. Both of these show conversational search at work.
Hummingbird really changes the keyword game quite a bit. Over time, exact keyword matches will no longer be such a big deal. The impact of this algorithm is likely to be quite substantial over the next two or so years. Net-net, they have drastically reduced access to the raw data, and are rolling out technology that changes the way it all works at the same time!
Google launched Google+ June 28, 2011. While it seemed to get off to a slow start initially, many argue that it has developed a lot of momentum and is growing rapidly. The data on Google+'s market share is pretty hard to parse, but there are some clear impacts on search. In addition, you can also see posts from people on Google+ show up in the results too. This is true even if you perform your search in "incognito" mode. And, while a link in a Google+ share isn't treated like a regular web link, it does have some SEO value when combined with other factors.How Google+ fits into this picture is that it was built from the ground up to be a content sharing network that helps with establishing "identities" and "semantic relevance." It does this quite well and there is a ton of activity in all kinds of different verticals on Google+.
Authorship also isn't new (launched on June 7, 2011), but it is a part of a bigger picture. Google can use this to associate new pieces of content with the person who wrote it. Over time, this data can be potentially used to measure which authors write stuff that draw a very strong response (links, social shares, +1s, comments) and give them a higher "Author Rank" (note that Google doesn't use this term, but those of us in the industry do). That said, in the future you can imagine that Google could use this as a ranking signal for queries where more comprehensive articles are likely to be a good response. Bottom line: your personal authority matters. Publisher Rank, the concept of building a site's authority,is arguably more important. Getting this payoff depends on a holistic approach to building your authority.
Google announced a new feature, in-depth articles August 6, 2013. The Google announcement included a statement that "up to 10% of users' daily information needs involve learning about a broad topic." That is a pretty big number and over time that this feature will become a pretty big deal. Effectively, this is an entirely new type of way to rank in the SERPs.This increases the payoff from Author Rank and Publisher Rank – there is a lot to be gained by developing both of these, assuming that Google actually does make it a ranking factor at some point. The data they have taken away has been historically used by publishers to optimize their SEO efforts in a very tactical manner.
On the other side of the coin, the major Google changes listed above are all moves that encourage more strategic behavior. All of these new pieces play a role in getting people to focus on their authority, semantic relevance, and the user experience. Again, this is what Google wants.
For clarity, no one is saying that Google designed these initiatives specifically to stop people from being tactical and make them strategic. It may simply be the case that Google operates from a frame of reference that they want to find and reward outstanding sites, pages, and authors that offer outstanding answers to user's search queries. But the practical impact is the same. The focus now is on understanding your target users, producing great content, establishing your authority and visibility, and providing a great experience for the users of your site. Properly architecting your site so that the search engines can understand it, including using schema and related markup, addressing local search (if that is relevant to you), and work of this type still matters, too. But, the obsession with tactical items like PageRank and keywords is going to fade away. As Google tweaks the way their service operates, and look for ways to capture new signals, they do things that naturally push you in that direction. It isn't going to stop. Expect more of the same going forward!
Hummingbird really changes the keyword game quite a bit. Over time, exact keyword matches will no longer be such a big deal. The impact of this algorithm is likely to be quite substantial over the next two or so years. Net-net, they have drastically reduced access to the raw data, and are rolling out technology that changes the way it all works at the same time!
Google launched Google+ June 28, 2011. While it seemed to get off to a slow start initially, many argue that it has developed a lot of momentum and is growing rapidly. The data on Google+'s market share is pretty hard to parse, but there are some clear impacts on search. In addition, you can also see posts from people on Google+ show up in the results too. This is true even if you perform your search in "incognito" mode. And, while a link in a Google+ share isn't treated like a regular web link, it does have some SEO value when combined with other factors.How Google+ fits into this picture is that it was built from the ground up to be a content sharing network that helps with establishing "identities" and "semantic relevance." It does this quite well and there is a ton of activity in all kinds of different verticals on Google+.
Authorship also isn't new (launched on June 7, 2011), but it is a part of a bigger picture. Google can use this to associate new pieces of content with the person who wrote it. Over time, this data can be potentially used to measure which authors write stuff that draw a very strong response (links, social shares, +1s, comments) and give them a higher "Author Rank" (note that Google doesn't use this term, but those of us in the industry do). That said, in the future you can imagine that Google could use this as a ranking signal for queries where more comprehensive articles are likely to be a good response. Bottom line: your personal authority matters. Publisher Rank, the concept of building a site's authority,is arguably more important. Getting this payoff depends on a holistic approach to building your authority.
Google announced a new feature, in-depth articles August 6, 2013. The Google announcement included a statement that "up to 10% of users' daily information needs involve learning about a broad topic." That is a pretty big number and over time that this feature will become a pretty big deal. Effectively, this is an entirely new type of way to rank in the SERPs.This increases the payoff from Author Rank and Publisher Rank – there is a lot to be gained by developing both of these, assuming that Google actually does make it a ranking factor at some point. The data they have taken away has been historically used by publishers to optimize their SEO efforts in a very tactical manner.
On the other side of the coin, the major Google changes listed above are all moves that encourage more strategic behavior. All of these new pieces play a role in getting people to focus on their authority, semantic relevance, and the user experience. Again, this is what Google wants.
For clarity, no one is saying that Google designed these initiatives specifically to stop people from being tactical and make them strategic. It may simply be the case that Google operates from a frame of reference that they want to find and reward outstanding sites, pages, and authors that offer outstanding answers to user's search queries. But the practical impact is the same. The focus now is on understanding your target users, producing great content, establishing your authority and visibility, and providing a great experience for the users of your site. Properly architecting your site so that the search engines can understand it, including using schema and related markup, addressing local search (if that is relevant to you), and work of this type still matters, too. But, the obsession with tactical items like PageRank and keywords is going to fade away. As Google tweaks the way their service operates, and look for ways to capture new signals, they do things that naturally push you in that direction. It isn't going to stop. Expect more of the same going forward!


